What Is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer occurs when a tumor grows inside one of your lungs. The cancer can spread to other parts of your body. It's important to catch the cancer early.
Computed tomography is the standard screening test for lung cancer. People who have smoked a pack a day for 20 years, or two packs for 10 years, should be tested.
If you have symptoms of lung cancer, the results of screening or procedures may find or rule out lung cancer. You may even require additional tests.

You can get lung cancer if you smoke — or if you never smoked. If you have symptoms or have been diagnosed, it's important to find out your options quickly.

If you are concerned about lung cancer, have been diagnosed with cancer, or are caring for someone with cancer, you will have questions. Here are some basics to start.
Lung cancer surgery involves removing a tumor from your lung, and often part or all of your lung. Here's what you should know about surgery for lung cancer.

Treatment of lung cancer depends on many factors, such as the type of cancer, its location, your overall health, and whether the cancer has spread.

If you're caring for someone with lung cancer, learn all you can. Knowledge builds confidence, but be sure to avoid information overload. Here's what you should know.
While smoking is still the main risk factor for lung cancer, 12 percent of lung cancer patients never smoked. Air pollution and genes increase your risk.
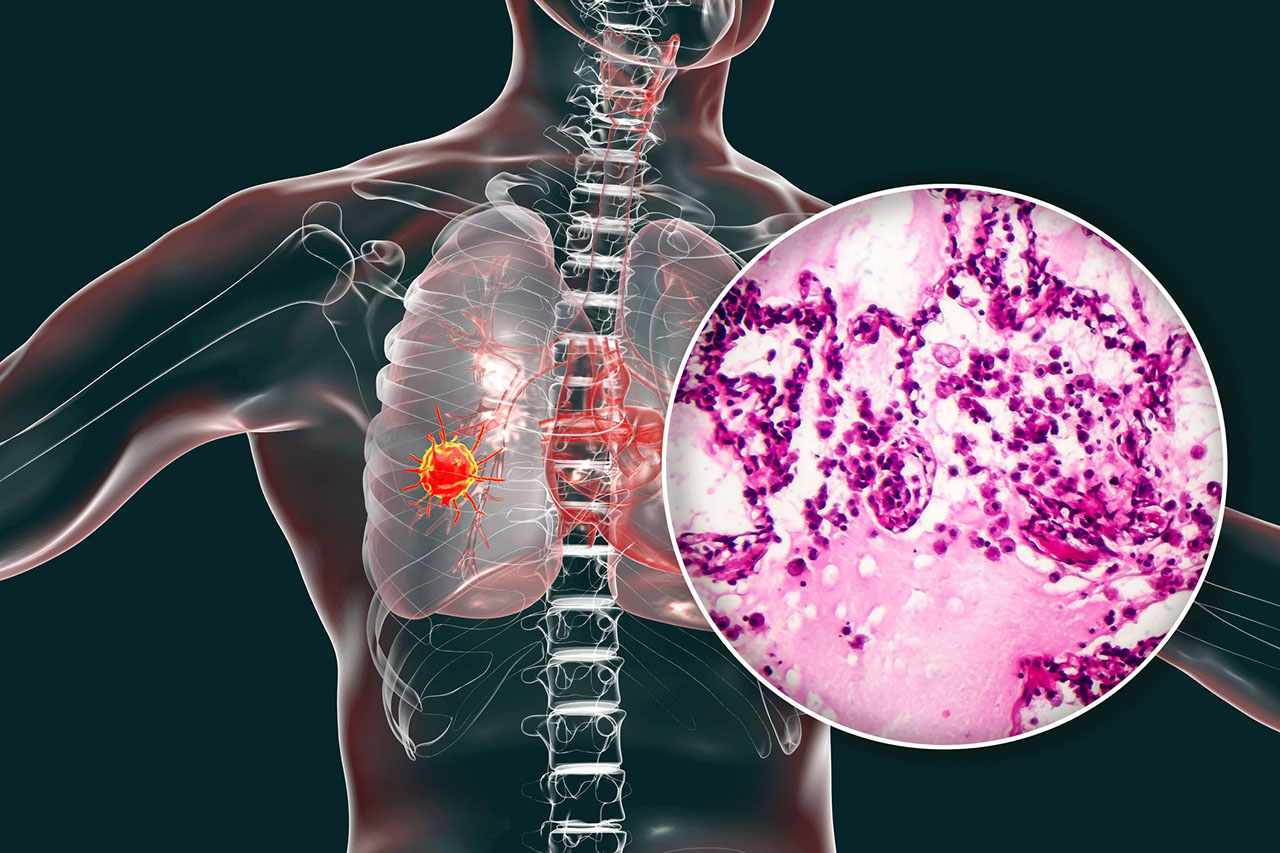
Most people don’t get potentially life-saving lung cancer tests, but if you smoke you may be eligible for a free screening. Here’s what you should know.