Is Walking Pneumonia Contagious?
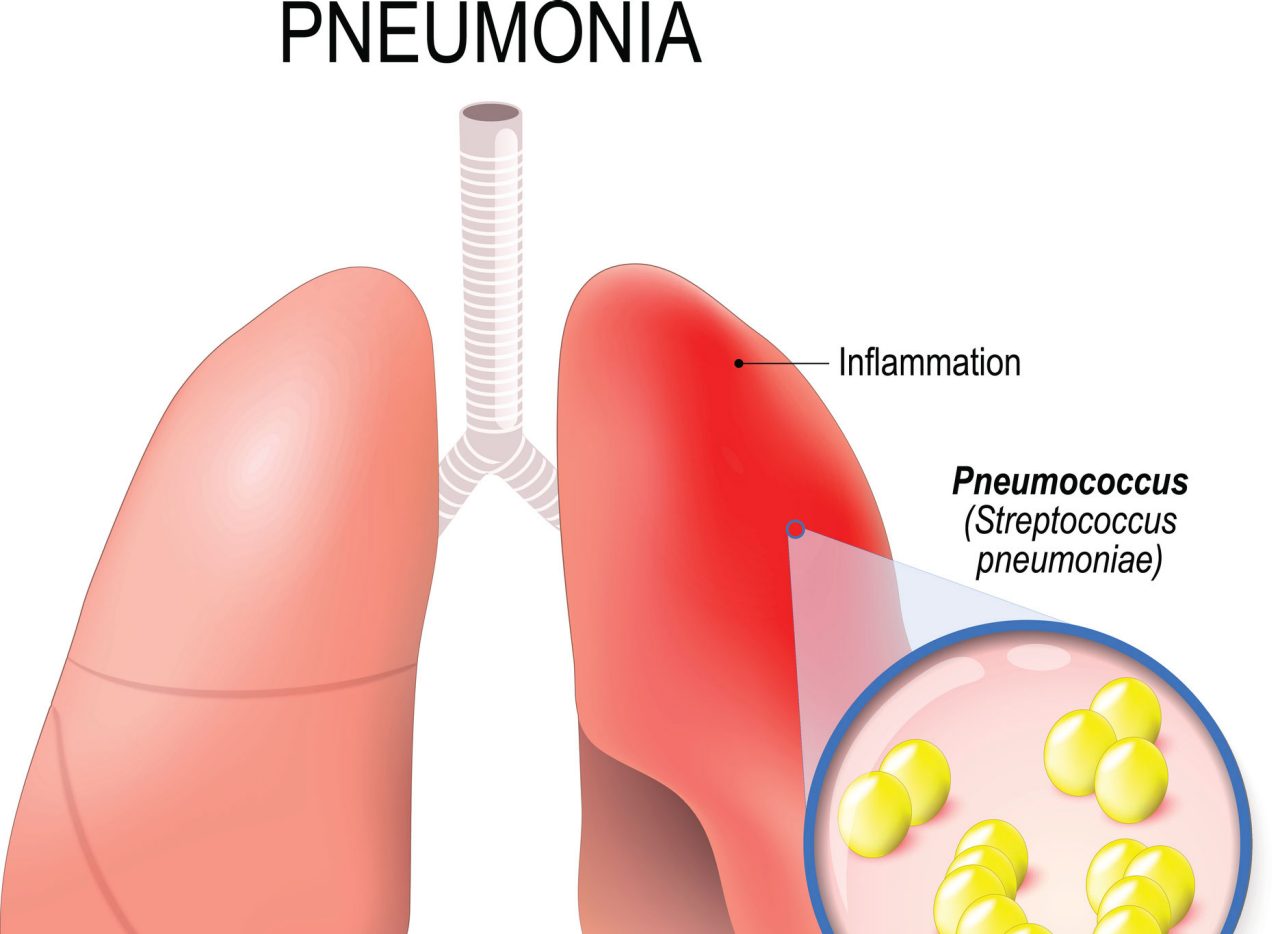
Also called atypical pneumonia, walking pneumonia is mild, and you'll usually avoid hospitalization. But it is highly contagious. Here's what you should know.
Imagine having an illness and not knowing about it. Walking pneumonia can make you feel miserable at times. At others, you may not even be aware you have the disease. Walking pneumonia or atypical pneumonia affects your upper and lower respiratory tract and is different from more serious types of pneumonia.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE: Our Cold and Flu Season section
What is walking pneumonia, and is walking pneumonia contagious?
A bacterial infection causes walking pneumonia. It often feels like a common cold. That means you can be walking around spreading the disease because you don’t know that you have it. About 2 million people in the U.S. get walking pneumonia each year. The illness lasts between a week and a month.
It affects people at any age. If you have school-age children and your child contracts walking pneumonia, he or she will be asked to stay home because walking pneumonia spreads easily. You can get it if you come into contact with droplets from an infected person’s sneeze or cough.
“Most patients with walking pneumonia are contagious for up to 10 days after onset of symptoms,” said Lokesh Guglani, MD, at University Pediatricians Children’s Hospital of Michigan.
According to Guglani, walking pneumonia symptoms usually appear between 15 and 25 days after exposure to the illness and can take two to four days to develop.
Walking pneumonia symptoms
- A cough that comes in violent spasms and produces almost no mucus
- Mild flu-like symptoms, such as a fever and chills
- A sore throat
- A headache
- Exhaustion, similar to feeling like you have the flu
- Weakness that lasts for several days
- Chest pain
- Vomiting
- Possible ear infections, a skin rash, and anemia
Types of walking pneumonia
- Mycoplasma pneumonia is the most common and mildest form of the disease.
- Chlamydial pneumonia is especially common among school-age children.
- Legionella pneumonia, also known as Legionnaire’s disease, is the most serious type of walking pneumonia. Left untreated, it can lead to respiratory failure and death. It mostly affects older adults, people with chronic illnesses, and those with weakened immune systems. It’s also contagious but doesn’t spread from person to person; it’s spread from contaminated water.
If you think you have signs, talk to your doctor. Your doctor will perform a physical exam, ask about your symptoms, and conduct a tests to see if you have it.
Tests for pneumonia
- Taking a culture of mucus from your lungs
- Sputum gram stain study, a mixture of your saliva and mucus that is examined under a microscope
- Throat swab
- Complete blood count, or CBC
- Study for specific antigens or antibodies
- Blood culture test
Walking pneumonia treatment
If tests come back positive, you can often treat pneumonia at home with antibiotics. If you get the rarer Legionella pneumophila, you’ll be hospitalized and put on antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and respiratory therapy if you have difficulty breathing.
If you have pneumonia, you should rest at home, take all of the antibiotics your doctor prescribed, and drink plenty of liquids. Walking pneumonia is highly contagious during the 10-day period of when your symptoms are most severe; it’s best to avoid contact with other people so you don’t infect them.
It’s possible for pneumonia to recur. To avoid and prevent a recurrence, or getting it in the first place, wash your hands, keep your hands away from your face after coming into contact with others, and cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you sneeze or cough. If you don’t have a tissue, sneeze or cough into the inside of your elbow, so you won’t spread it to others.
Updated:
September 29, 2023
Reviewed By:
Janet O’Dell, RN